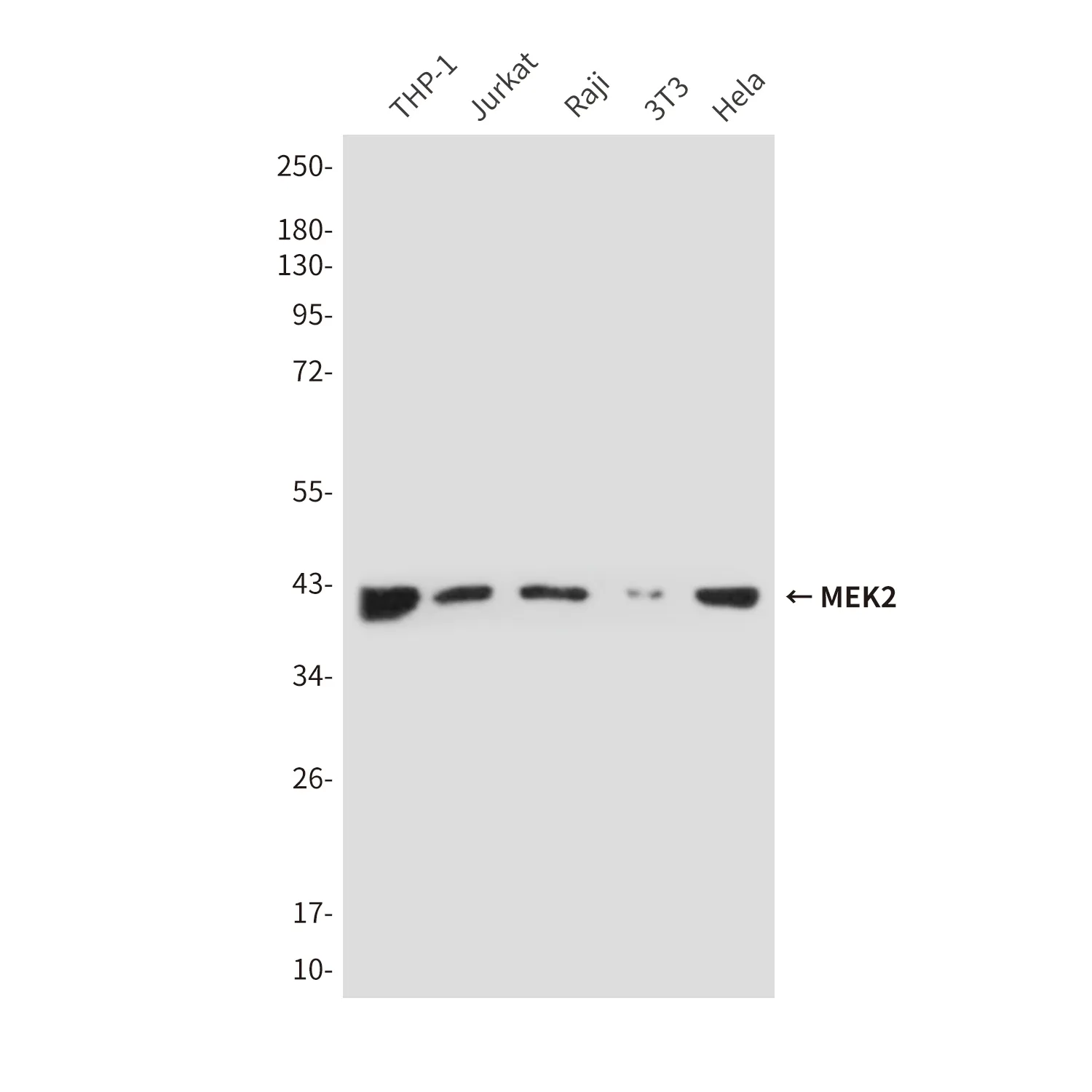
Summary
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
Adapter protein implicated in the regulation of a large spectrum of both general and specialized signaling pathways. Binds to a large number of partners, usually by recognition of a phosphoserine or phosphothreonine motif. Binding generally results in the modulation of the activity of the binding partner. When bound to KRT17, regulates protein synthesis and epithelial cell growth by stimulating Akt/mTOR pathway. Adapter protein implicated in the regulation of a large spectrum of both general and specialized signaling pathways. Binds to a large number of partners, usually by recognition of a phosphoserine or phosphothreonine motif. Binding generally results in the modulation of the activity of the binding partner. When bound to KRT17, regulates protein synthesis and epithelial cell growth by stimulating Akt/mTOR pathway. May also regulate MDM2 autoubiquitination and degradation and thereby activate p53/TP53.
Research Area