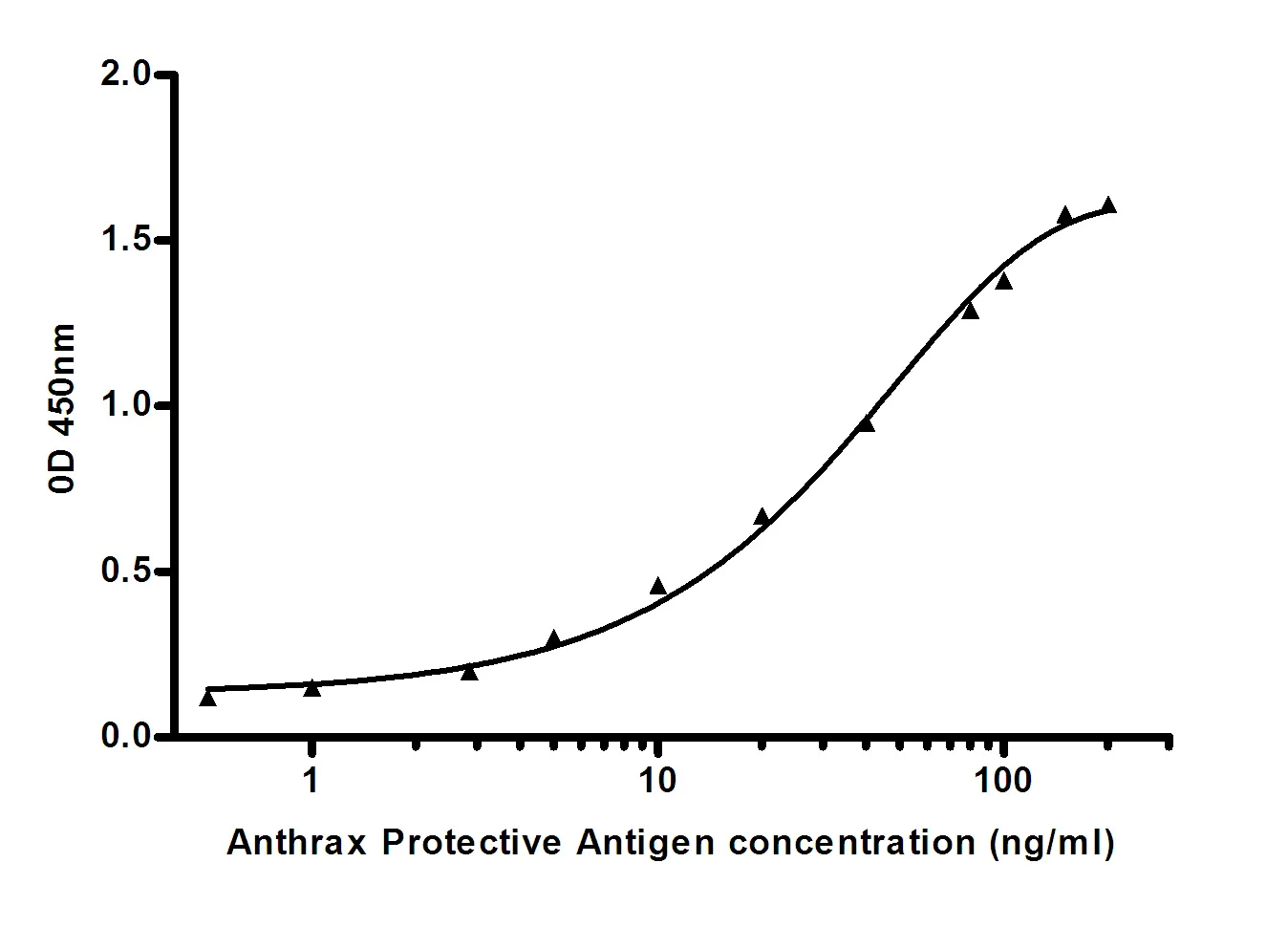
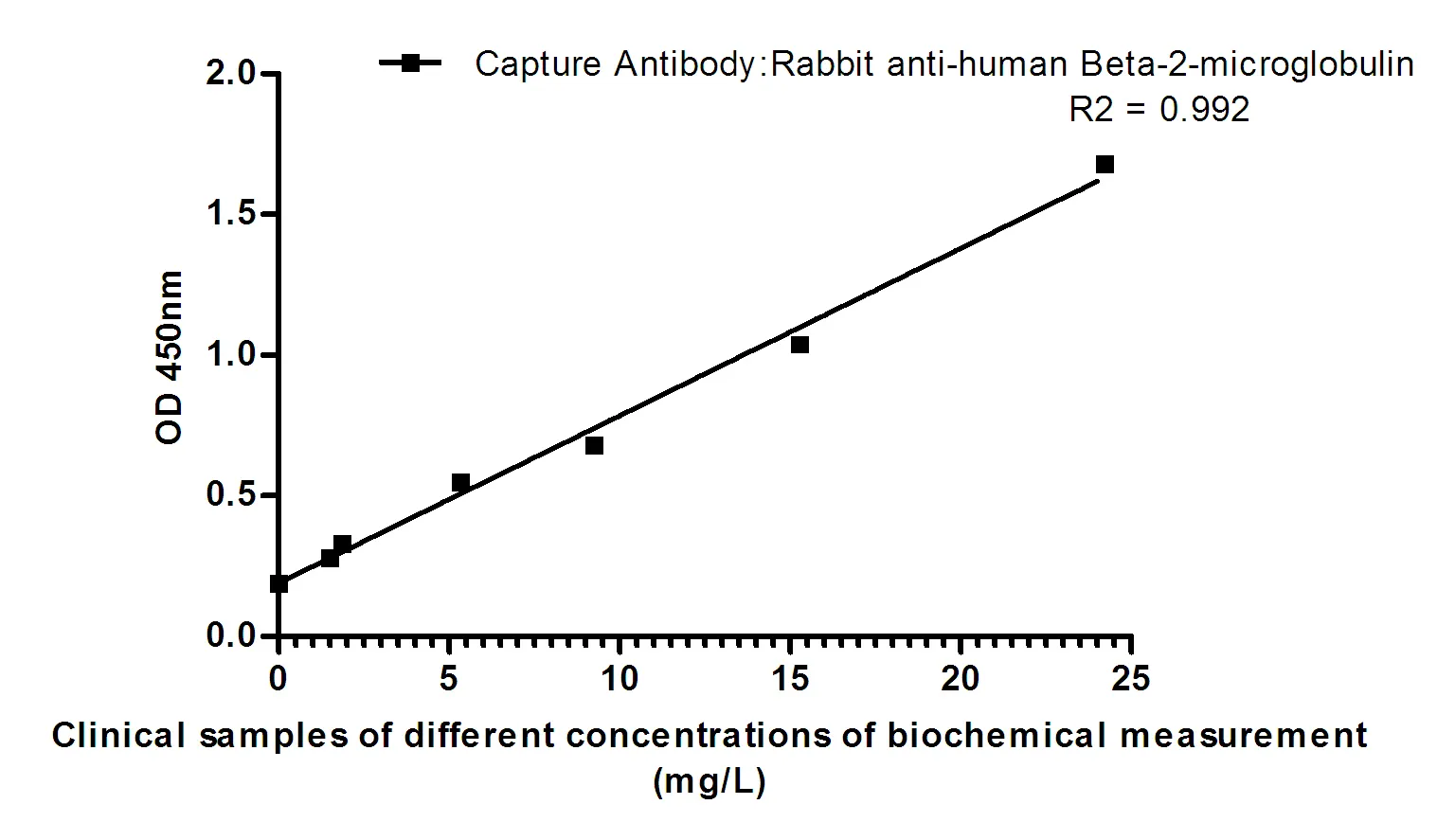
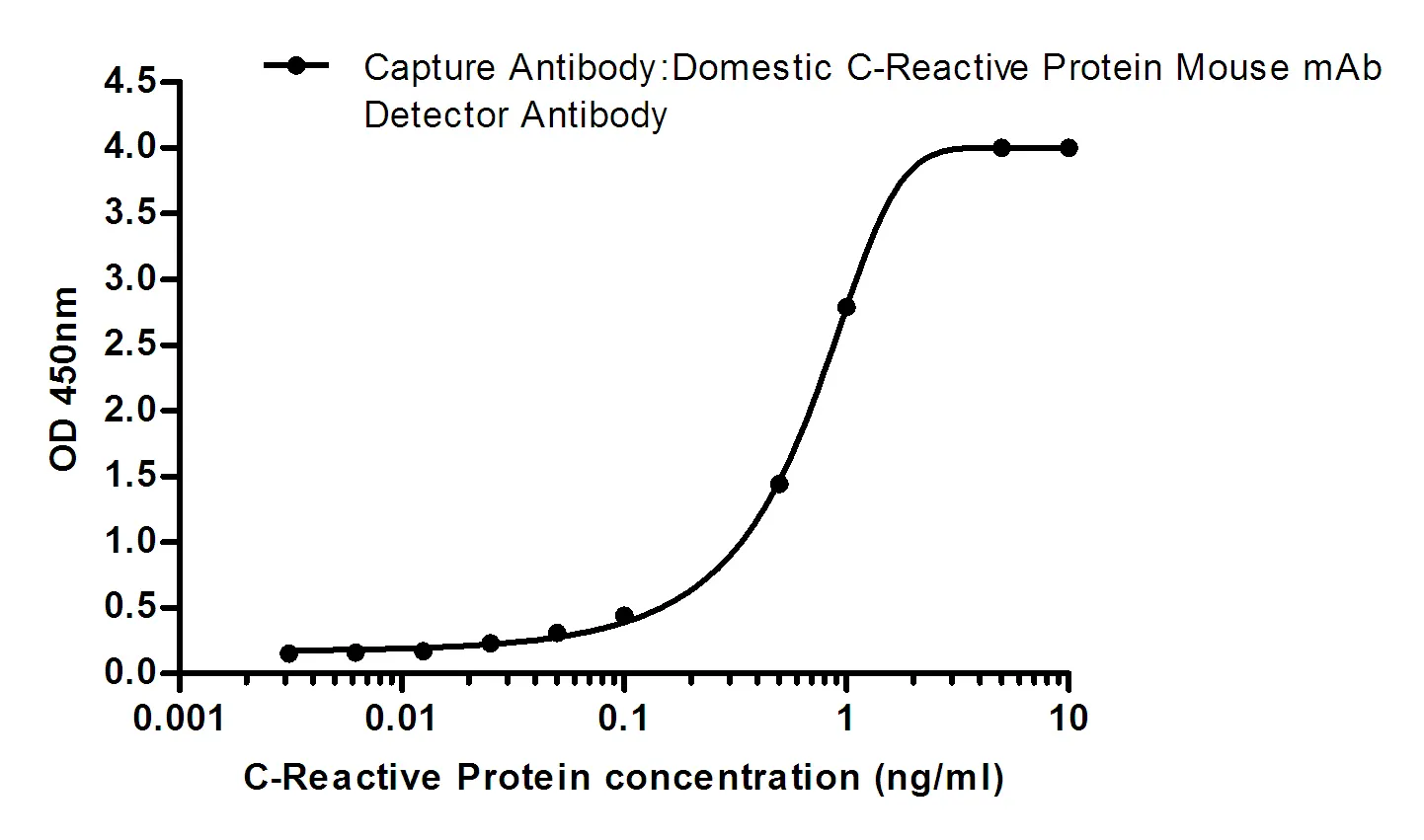
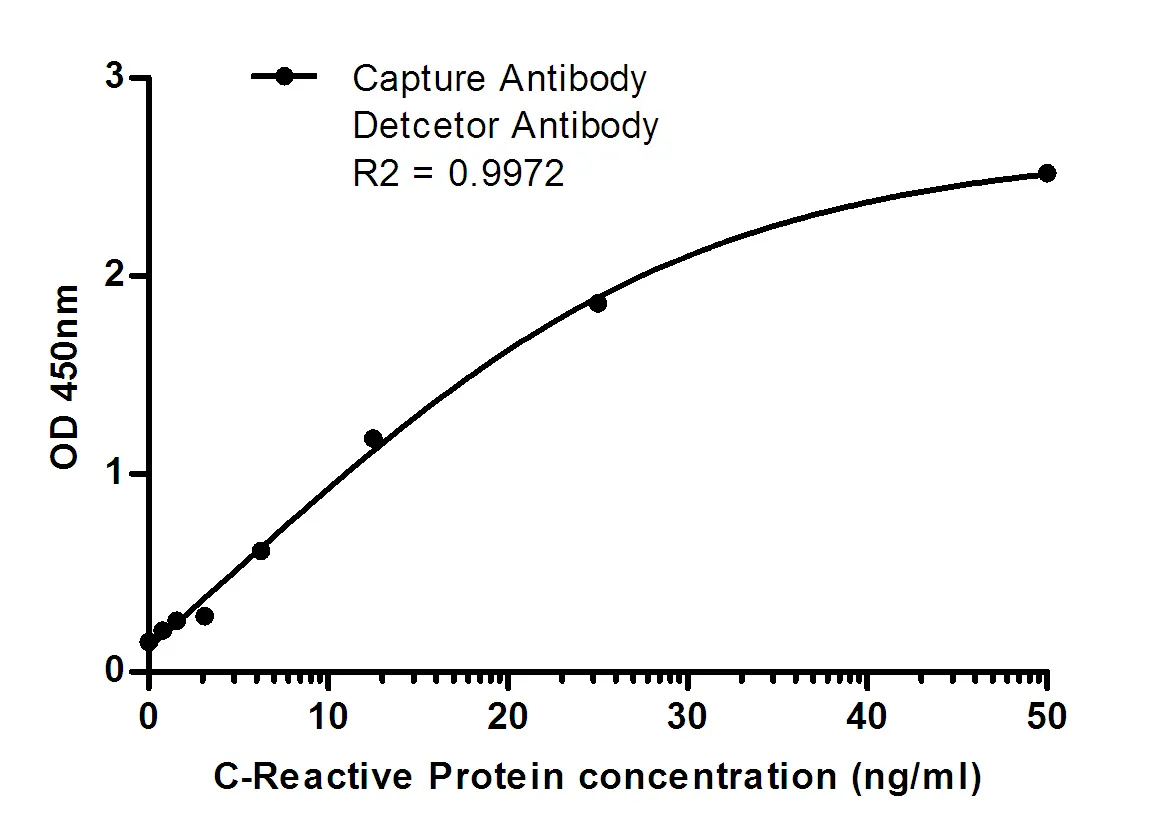
Summary
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
The protein encoded by this gene functions together with DNA ligase IV and the DNA-dependent protein kinase in the repair of DNA double-strand breaks. This protein plays a role in both non-homologous end joining and the completion of V(D)J recombination. Mutations in this gene can cause short stature, microcephaly, and endocrine dysfunction (SSMED). Alternative splicing generates several transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015],function:Involved in DNA non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) required for double-strand break repair and V(D)J recombination. Binds to DNA and to DNA ligase IV (LIG4). The LIG4-XRCC4 complex is responsible for the NHEJ ligation step, and XRCC4 enhances the joining activity of LIG4. Binding of the LIG4-XRCC4 complex to DNA ends is dependent on the assembly of the DNA-dependent protein kinase complex DNA-PK to these DNA ends.,PTM:Monoubiquitinated.,PTM:Phosphorylated by PRKDC. The phosphorylation seems not to be necessary for binding to DNA. Phosphorylation by CK2 promotes interaction with APTX.,PTM:Sumoylation at Lys-210 is required for nuclear localization and recombination efficiency. Has no effect on ubiquitination.,similarity:Belongs to the XRCC4 family.,subunit:Homodimer and homotetramer in solution. The homodimer associates with LIG4, and the LIG4-XRCC4 complex associates in a DNA-dependent manner with the DNA-PK complex formed by the Ku p70/p86 dimer (G22P1/G22P2) and PRKDC. Seems to interact directly with PRKDC but not with the Ku p70/86 dimer. Interacts with XLF/Cernunnos. Interacts with APTX and APLF.,tissue specificity:Widely expressed.,
Research Area
Non-homologous end-joining;