Summary
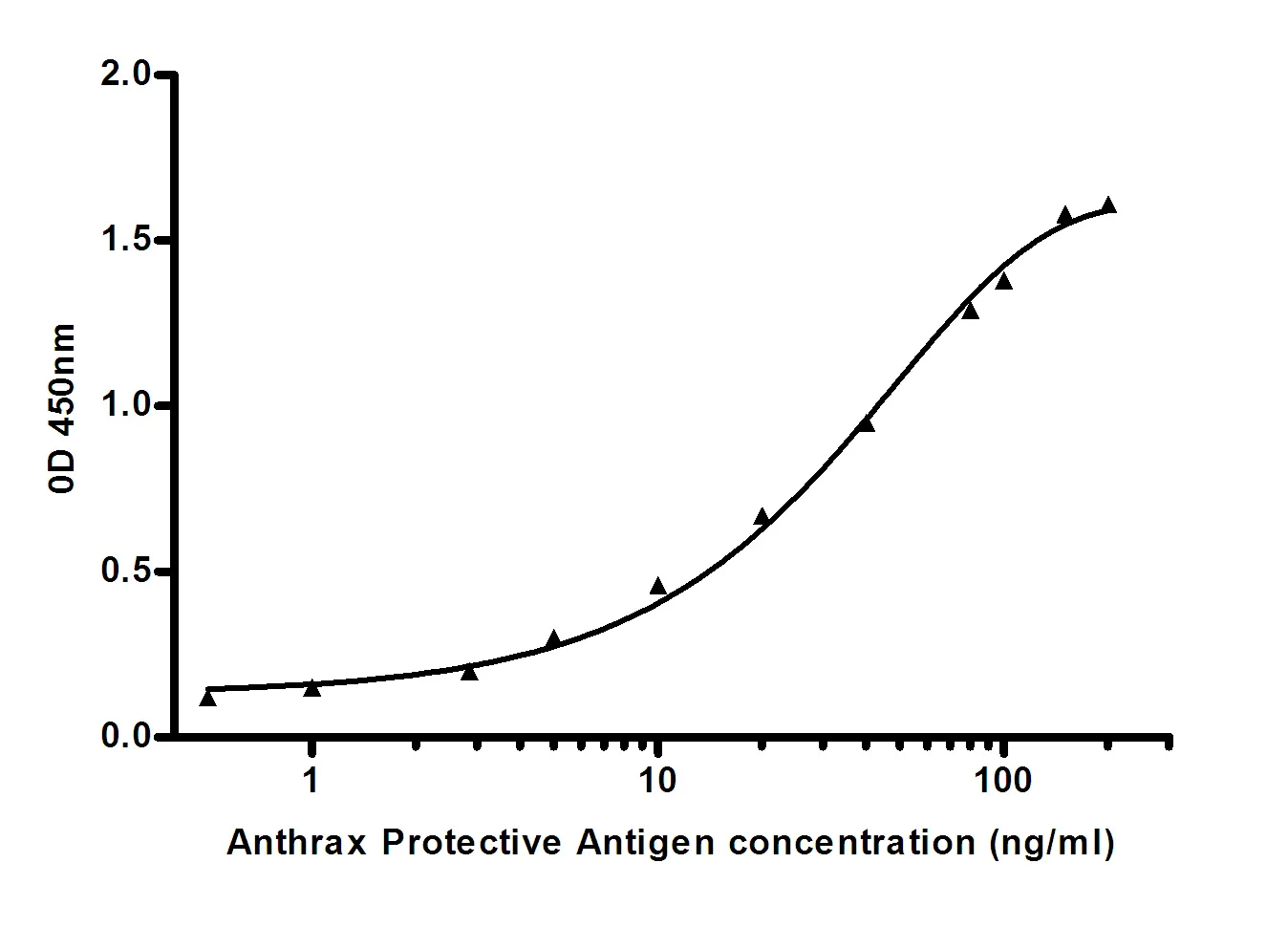
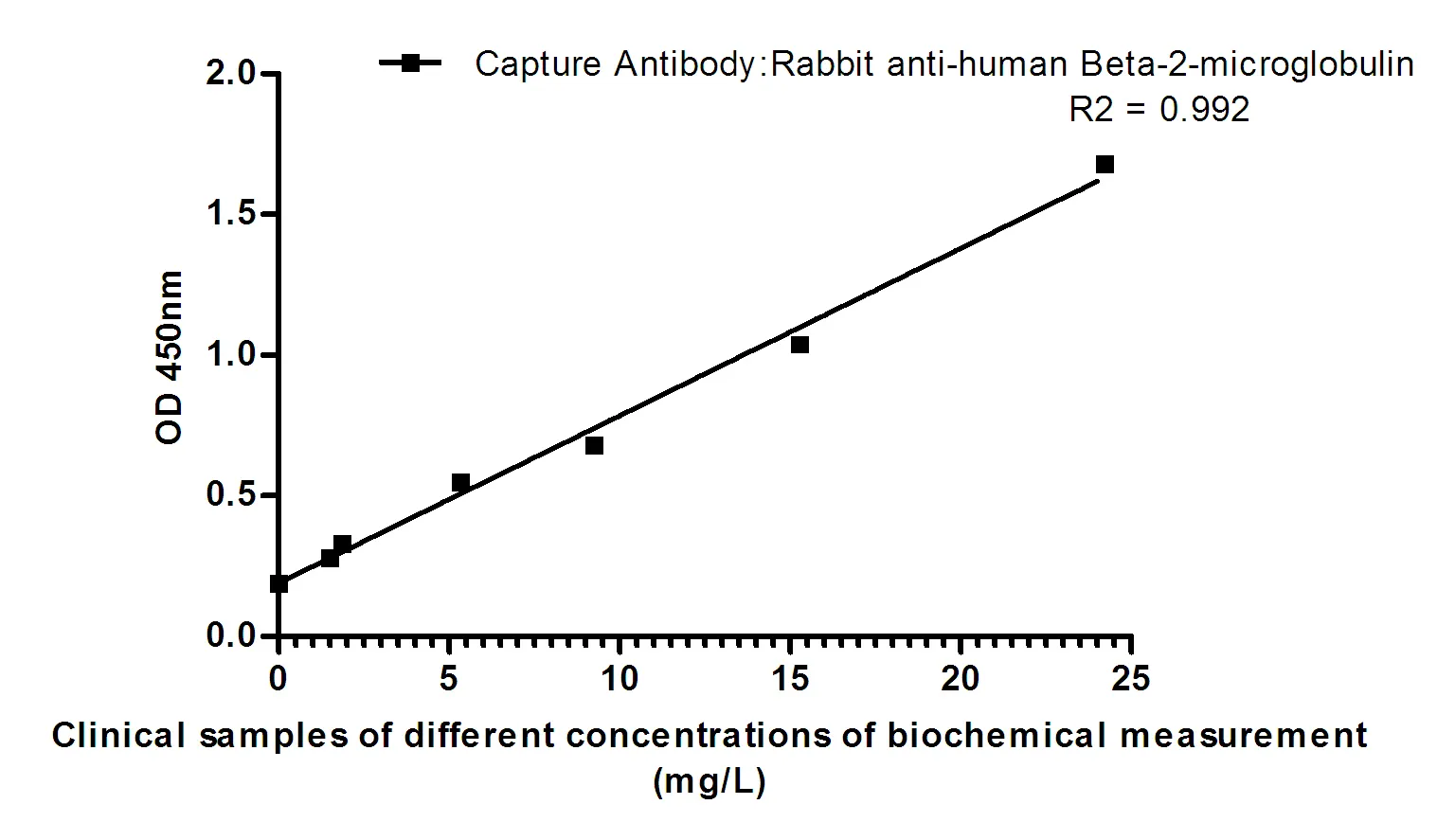
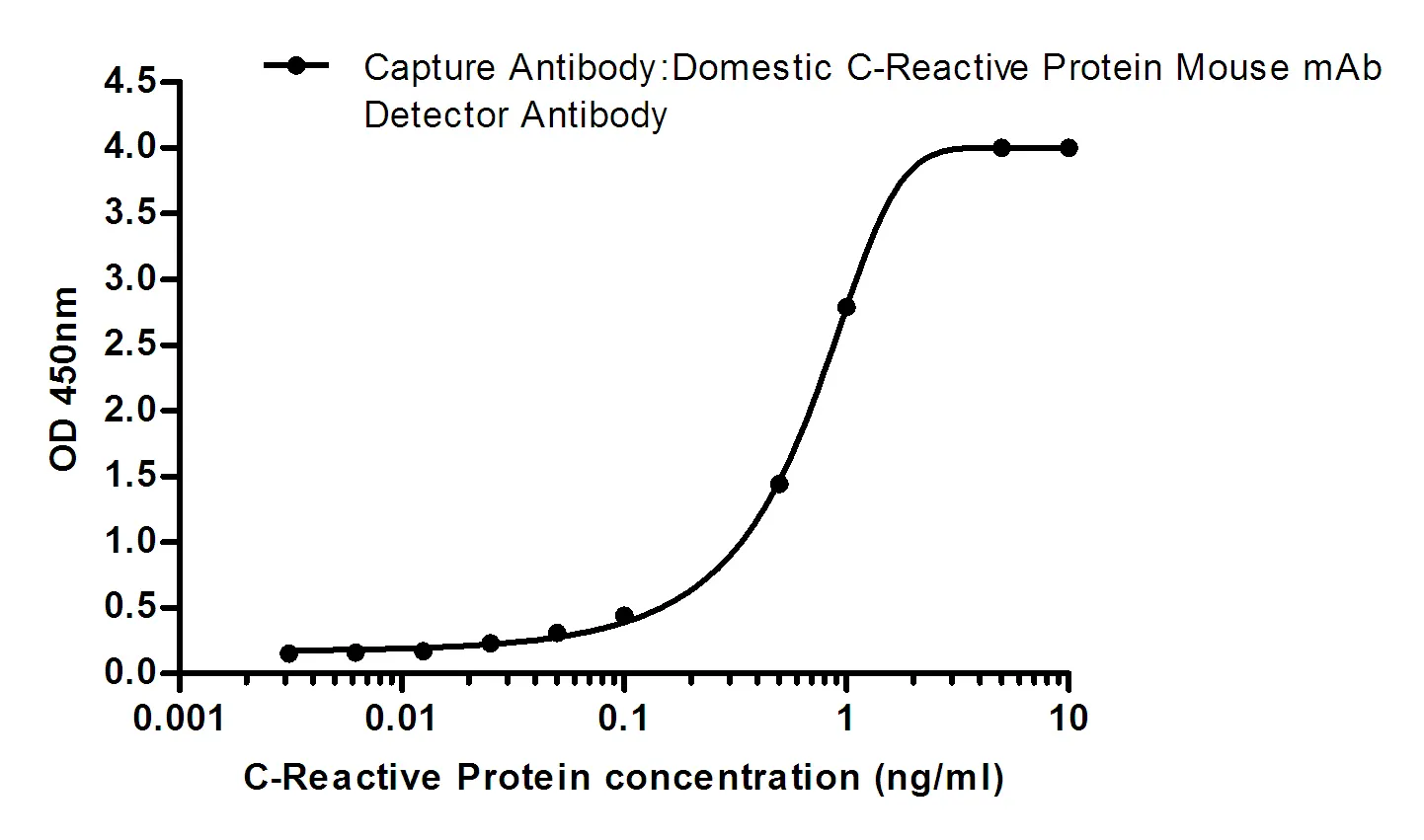
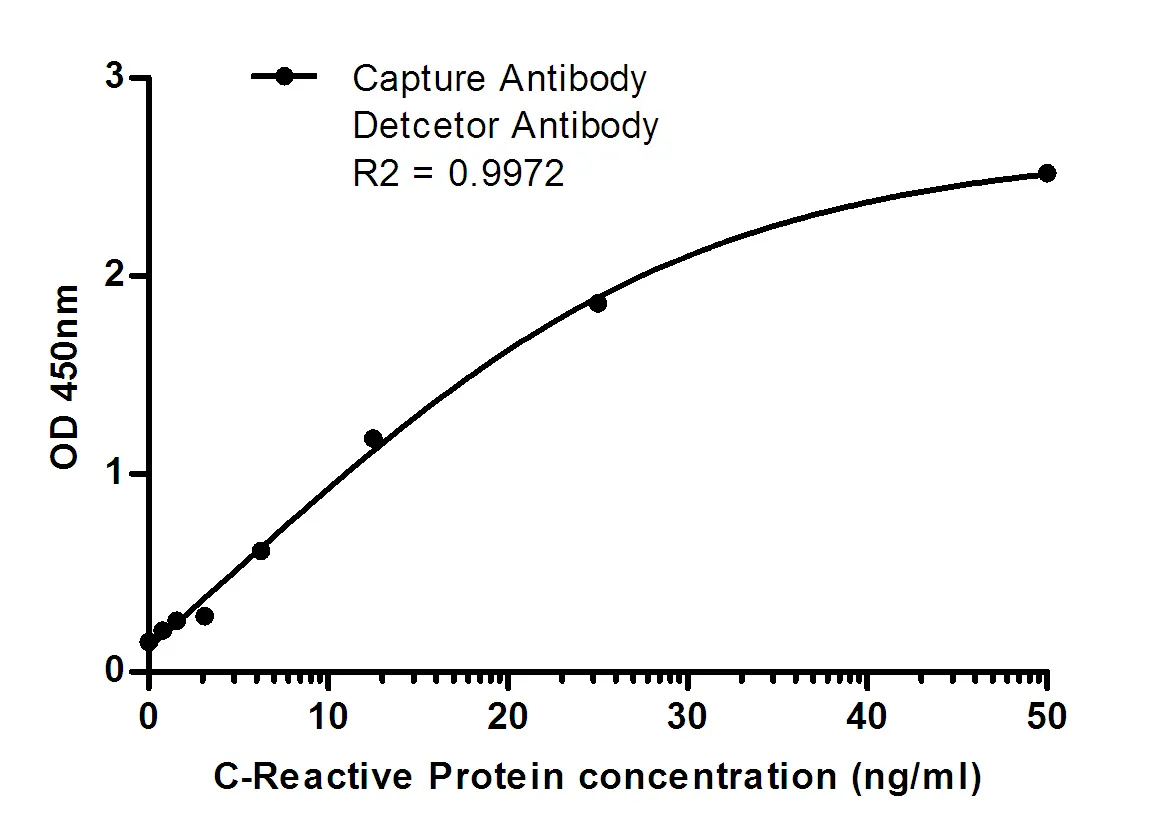
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
This gene encodes a cell surface tyrosine kinase receptor for members of the platelet-derived growth factor family. These growth factors are mitogens for cells of mesenchymal origin. The identity of the growth factor bound to a receptor monomer determines whether the functional receptor is a homodimer or a heterodimer, composed of both platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha and beta polypeptides. Studies suggest that this gene plays a role in organ development, wound healing, and tumor progression. Mutations in this gene have been associated with idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome, somatic and familial gastrointestinal stromal tumors, and a variety of other cancers. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012],catalytic activity:ATP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine = ADP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine phosphate.,disease:A fusion of PDGFRA and FIP1L1 (FIP1L1-PDGFRA), due to an interstitial chromosomal deletion, is the cause of some cases of hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) [MIM:607685]. HES is a rare hematologic disorder characterized by sustained overproduction of eosinophils in the bone marrow, eosinophilia, tissue infiltration and organ damage.,function:Receptor that binds both PDGFA and PDGFB and has a tyrosine-protein kinase activity.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. CSF-1/PDGF receptor subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 protein kinase domain.,similarity:Contains 5 Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains.,subunit:Homodimer, and heterodimer with PDGFRB. Interacts with the SH2 domain of SHB via phosphorylated Tyr-720 (By similarity). Interacts with the SH2 domain of SHF via phosphorylated Tyr-720.,tissue specificity:Expressed in primary and metastatic colon tumors and in normal colon tissue. Tumors may express a different isoform to that found in normal tissue.,
Research Area
MAPK_ERK_Growth;MAPK_G_Protein;Calcium;Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction;Endocytosis;Focal adhesion;Gap junction;Regulates Actin and Cytoskeleton;Pathways in cancer;Colorectal cancer;Glioma;Prostate cancer;Melanoma;